A cooling tower is used to cool and circulate water used in settings such as oil refineries petrochemical and other chemical plants thermal power stations and hvac systems for cooling buildings.
Closed circuit cooling water system in power plant.
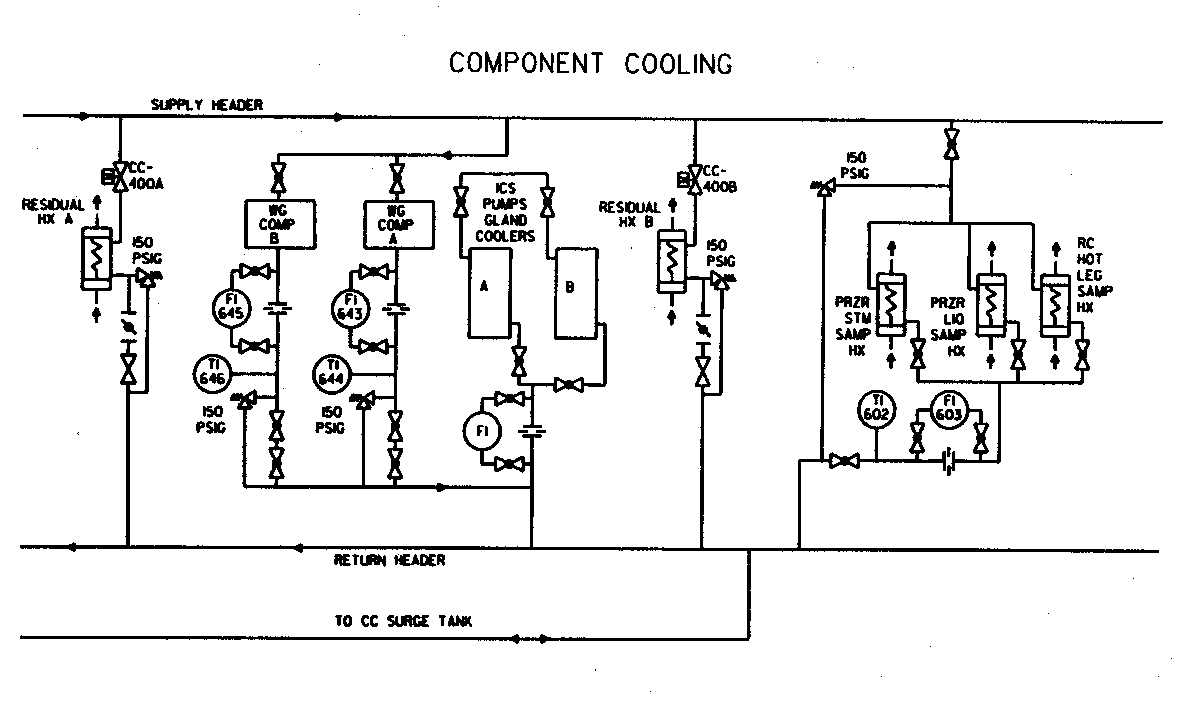
But often overlooked are auxiliary closed cooling water ccw systems which also serve vital functions.
Power plants located away from large sources of water utilise.
Failure of a closed system has the potential to shut down a portion if not all of the plant.
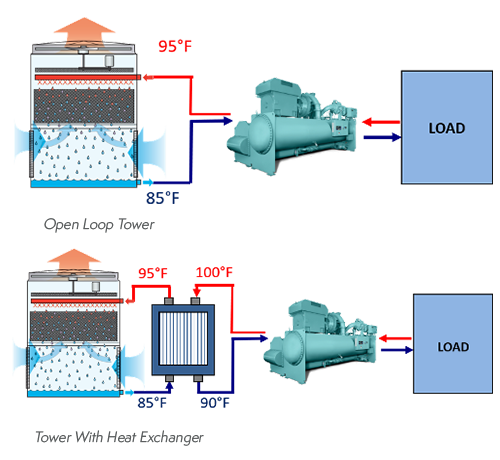
Cooling towers extract waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a water stream to a lower temperature.
Some of the water evaporates.
The second function for water in such a power plant is to cool the system so as to condense the low pressure steam and recycle it.
This feature is not available right now.
In the cooling towers an airflow natural or forced cools the water and the water returns to the condenser.
The circulating water removes the heat from the condenser and flows to cooling towers.
Closed cooling water system in power plant.
Using a cooling system reduces the heat wear on these components and a.
Closed systems are also widely used in air conditioning chilled water systems to transfer the refrigerant cooling to air washers in which the air is chilled.
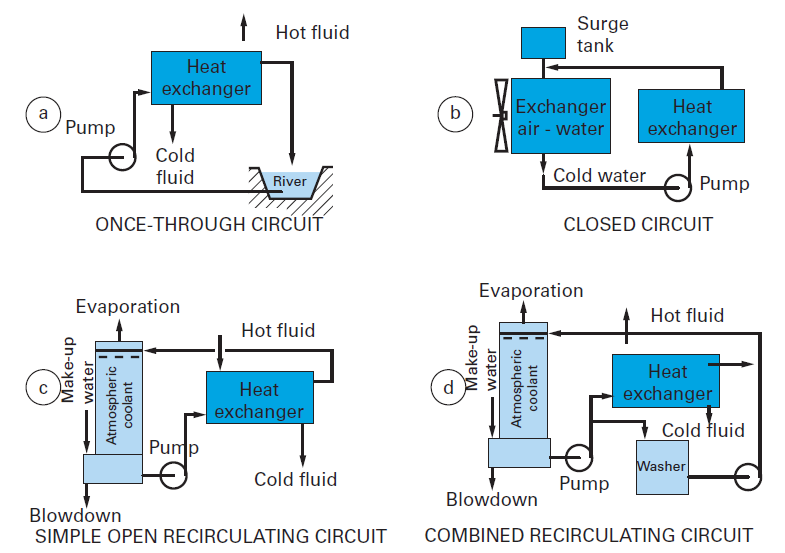
There are two different types.
Other closed recirculating cooling applications include smelt spout cooling systems on kraft recovery boilers and lubricating oil and sample coolers in power plants.
P rimary cooling at steam generating power plants and many other heavy industries is a critical aspect of operation and upsets can cost a great deal in lost efficiency and production.
The rest is then sent back to the condenser in the power plant.
Wet recirculating or closed loop systems reuse cooling water in a second cycle rather than immediately discharging it back to the original water source.
Please try again later.
Aside from emergency use closed circuit cooling systems also serve to cool down components at a power plant.
Cooling towers may either use the evaporation of water to remove process heat and cool the working fluid to near the wet bulb air temperature or in the case of closed circuit dry cooling towers rely solely on air to cool the working fluid to near.
At a power plant the moving parts can generate enormous amounts of heat.
As the steam in the internal circuit condenses back to water the surplus waste heat which is removed from it needs to be discharged by transfer to the air or to a body of water.
Other closed loop cooling systems can include chilled water systems for air chillers used at the air inlet to the gas turbines at a combined cycle power plant and the chemistry sample panel.
A cooling tower is a heat rejection device that rejects waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a water stream to a lower temperature.